| Product: | Desmosine | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Catalog Number: | 5363 | ||||
| CAS Number: | 10019-68-8 | ||||
| Pricing: |
|
||||
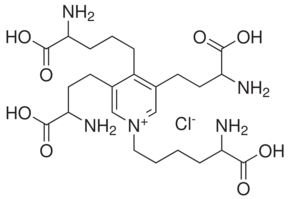
| Formula: | C24H40ClN5O8 | ||||
| Molecular Weight: | 562.06 | ||||
| Structure: |
|
||||
| Appearance: | Solid | ||||
| Category: | Unlabeled Reference Standards | ||||
| Stability: | Stable under recommended storage conditions | ||||
| Storage: |
Keep container tightly closed in a dry and well-ventilated place. Recommended storage temperature: 2-8°C |
||||
| Transportation: |
Non-hazardous for transport |
||||
| Literature References: |
Cocci, F., et al., Urinary desmosine excretion is inversely correlated with the extent of emphysema in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2002, 34:594-604; Cantor, J.O., et al., Measurement of cross-linked elastin synthesis in bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis using a highly sensitive assay for desmosine and isodesmosine J. Lab. Clin. Med., 1984, 103:384-392; Mecham, R.P., and Foster, J.A., A structural model for desmosine cross-linked peptides Biochem. J., 1978, 103:617-625.; Cocci F., et al., Urinary desmosine excretion is inversely correlated with the extent of emphysema in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol., 2002, 34:594-602.; Basalyga DM., et al., Elastin degradation and calcification in an abdominal aorta injury model: role of matrix metalloproteinases. Circulation, 2004, 110:3480-3487.; Bailey M., et al., Aluminum chloride pretreatment of elastin inhibits elastolysis by matrix metalloproteinases and leads to inhibition of elastin-oriented calcification. Am. J. Pathol., 2001, 159:1981-1986.; Starcher, B.C. and Galione, M.J. Prep. Biochem. 1975, 5:455. |
||||
| MSDS: | |||||
| Description: |
Assays for free or urinary desmosine are often used as markers for disease states characterized by elastin degradation (e.g., emphysema). Conversely, excessive levels of incorporated desmosine are indicators of fibrotic conditions (e.g., cirrhosis). Desmosine chloride is often used in assays for free or urinary desmosine as markers for disease states characterized by elastin degradation (e.g., emphysema). Elastin degradation has shown strong correlation with vascular calcification, and pretreatment with aluminum ions can inhibit the binding of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) to elastin. Desmosine is a polyfunctional amino acid that forms cross-links in mature elastin. |
